How High Did The Water Get During Helene? Unpacking The Storm's Impact
When Hurricane Helene swept through, a lot of people started asking about the water. It's a natural thing to wonder, really, how much did the water rise? This question, "How high did the water get during Helene?", is more than just about a number; it's about what that height means for homes, for land, and for daily life. Understanding the true measure of the water's reach during such a powerful weather event helps us grasp the sheer force of nature, and that's pretty important, don't you think?
For many, the memory of Helene still feels quite real, and for good reason. The storm brought with it a tremendous amount of moisture, and that water had to go somewhere. So, people wanted to know, just how far up did it go? This isn't just a simple query; it speaks to the very heart of how communities cope with and recover from big storms. It's about figuring out the extent of the impact, and, you know, planning for what might come next.
We're going to explore what "high water" actually means in the context of a hurricane like Helene, and, in a way, break down the different elements that contributed to those water levels. We'll look at how these measurements are taken, what they tell us, and why it matters so much to those who lived through it. So, stick around, because there's quite a bit to unpack about those water marks.
- Did Delirious Leave The Vanoss Crew
- What Famous Person Is Julia Roberts Related To
- How Old Is Derek Hale In Season 1
Table of Contents
- Understanding What "High Water" Means
- Factors That Made the Water Rise During Helene
- Helene's Water Levels: What We Know
- The Impact of Elevated Water Levels
- Preparing for Future High Water Events
- Lessons Learned from Helene's Water Levels
- Frequently Asked Questions About Helene's Water
Understanding What "High Water" Means
When we talk about "high water" during a storm like Helene, it's not just about a simple number on a ruler. It really means something much more comprehensive. For instance, my text tells us that "high implies marked extension upward and is applied chiefly to things which rise from a base or foundation or are placed at a." So, when water gets "high," it's about how far it extends above its usual resting place, how much it rises from the ground or a normal water level. It's a measure of how much something is elevated, and that's a pretty important distinction, you know?
The Definition of "High" in This Context
My text goes on to explain that "high" can mean "having a relatively great elevation" or "a large distance above the ground." In the case of Helene, this means the water moved significantly above where it usually sits. It wasn't just a slight increase; it was a noticeable, and often impactful, surge upward. This concept of "high" also includes the idea of being "above the normal or average level," which is exactly what happens when a powerful storm pushes water inland. So, it's about the abnormal rise, in a way.
Understanding this definition helps us appreciate the full scope of what "high water" during Helene truly meant. It wasn't just about a river overflowing; it was about the ocean pushing inland, or vast amounts of rain creating new, temporary waterways. This kind of "high" water can reach places it never usually does, and that, too, is a critical part of the story.
Factors That Made the Water Rise During Helene
A hurricane's water levels aren't just from one source; they're a mix of several powerful forces working together. For Helene, this combination created a serious situation for many communities. Knowing what these factors are helps us understand why the water got as high as it did, and that's quite helpful for future planning, you see.
Storm Surge: A Major Player
One of the biggest contributors to "high water" during a hurricane is what's called storm surge. This is when the strong winds of the storm push ocean water onto land, above the normal tide level. It's not just a wave; it's a massive dome of water that comes ashore. For Helene, this meant coastal areas saw water levels rise very quickly, sometimes by many feet. This surge can be incredibly powerful, and it's often the most destructive part of a hurricane for those near the coast, you know.
The intensity of the storm, its size, and the shape of the coastline all play a part in how much storm surge occurs. A stronger storm, for instance, typically creates a more substantial surge. So, the characteristics of Helene itself were a big factor in how much water was pushed inland, and that's pretty clear.
Heavy Rainfall: Adding to the Volume
Beyond the ocean's push, hurricanes also bring immense amounts of rain. Helene was no exception. This rain falls continuously, sometimes for many hours, saturating the ground and causing rivers, lakes, and streams to swell. This is often called inland flooding, and it can happen far from the coast. So, even if you weren't right on the beach, the sheer volume of rain could still lead to very high water levels around you, and that's a real concern.
When the ground can't absorb any more water, and drainage systems get overwhelmed, the water has nowhere to go but up. This can turn streets into rivers and flood basements, making the "high water" problem much worse. It's a different kind of water rise than storm surge, but just as serious, you know.
Tides and Local Geography
The timing of a storm also matters a lot. If a hurricane's storm surge arrives during a high tide, the total water level will be even greater. It's like adding an extra layer of water on top of what's already there. So, the natural ebb and flow of the ocean played a part in how high the water got during Helene, too.
Local geography, like bays, inlets, and the slope of the land, also affects how water moves and accumulates. Some areas are naturally more prone to flooding because of their low elevation or the way water gets trapped. These geographical features, coupled with Helene's intensity, really shaped where the water went and how high it reached, and that's something to consider.
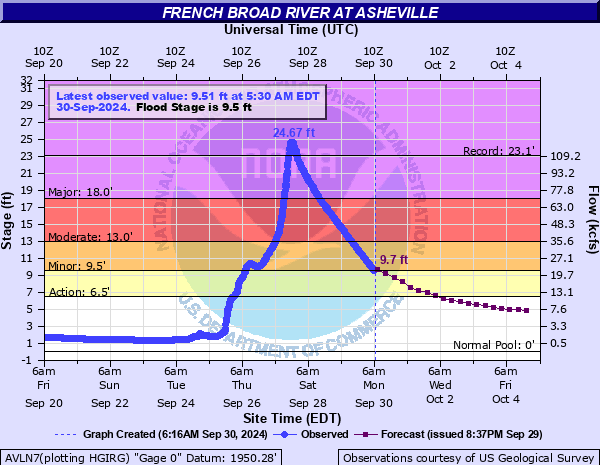
Helene's Water Levels: What We Know
Getting precise numbers on how high the water got during Helene can be a bit tricky because it varied so much from one place to another. What was a few feet in one town might have been significantly more in another, just a short distance away. But, there are ways we gather this information, and that's pretty helpful for everyone.
Reported Heights and Variations
Across the areas Helene affected, reports of water levels showed a wide range. Some coastal communities experienced storm surges that pushed water many feet above ground level, inundating homes and businesses. Inland, heavy rainfall caused rivers to overflow their banks, leading to significant flooding in low-lying areas. So, the "high" water wasn't uniform; it was a very localized experience for many.
For example, some areas might have seen water rise by a few feet, enough to cover roads and enter ground floors. Other places, particularly those directly in the path of the storm's strongest winds and surge, could have experienced water levels that were "tall," meaning they reached up to second stories or even higher. This variation really underscores how different the storm's impact could be even within a small region, and that's something to keep in mind.
How Water Heights Are Measured
To figure out "how high did the water get during Helene," scientists and emergency teams use various tools. Tide gauges, which are permanent sensors in coastal waters, provide continuous data on water levels. After a storm, survey teams often go out to find "high water marks" – things like debris lines on buildings or trees, or stains left on structures – to determine the peak water elevation. These marks are then measured relative to a fixed point, like sea level or the ground. So, it's a very systematic way of figuring things out.
Radar and satellite data also help estimate rainfall amounts, which contribute to inland flooding models. All this information is put together to create a comprehensive picture of the water's reach. It's a complex process, but it helps us get a clearer idea of the storm's true water footprint, and that's pretty cool, actually.
The Impact of Elevated Water Levels
The question of "how high did the water get during Helene?" isn't just about numbers; it's deeply connected to the consequences for people and places. When water reaches those elevated levels, it brings about a whole host of problems that communities have to deal with for a long time afterward. It's a very serious matter, you know.
Damage to Property and Infrastructure
High water levels from Helene caused widespread damage to buildings. Homes, businesses, and public structures that found themselves submerged faced structural issues, mold growth, and the loss of personal belongings. The water, especially if it was salty storm surge, can be incredibly corrosive and leave a terrible mess. So, the financial toll alone was quite significant for many, and that's just a part of it.
Beyond individual properties, infrastructure also took a big hit. Roads became impassable, bridges were compromised, and utility systems like electricity and sewage lines were disrupted. This kind of damage makes it really hard for emergency services to reach people and for communities to get back on their feet. It's a domino effect, in a way, that stems from that high water.
Effects on Daily Life and Safety
When the water gets high, daily life pretty much stops. People can't go to work or school, and access to essential services like food and medical care becomes difficult. There are also immediate safety concerns, like the risk of drowning, electrocution from downed power lines in water, and exposure to contaminated water. So, the immediate danger is very real, you see.
The long-term effects on mental well-being are also important. The stress of losing possessions, dealing with insurance claims, and rebuilding can be overwhelming. The memory of seeing water reach "a large distance above the ground" or "above a person or thing" can stay with people for a very long time. It really changes things for people, that's for sure.
Preparing for Future High Water Events
Learning from Helene's experience with high water levels is absolutely key for being ready for future storms. It's not about being scared, but about being smart and proactive. So, understanding what to do when water starts to rise is something everyone in vulnerable areas should think about, you know?
Understanding Your Risk
The first step in preparing is knowing if your home or community is in a flood-prone area. Flood maps are available from government agencies and show different flood zones. If you live in a low-lying area, or near a river or coast, your risk of experiencing "high" water is, of course, greater. So, taking the time to look at these maps is a very good idea, and that's a simple first step.
Understanding the difference between storm surge zones and rainfall flood zones is also helpful. While both involve water, they require slightly different preparations. Knowing your specific risk helps you make better decisions about things like flood insurance and evacuation plans. It's about being informed, and that's pretty powerful.
Steps to Take Before a Storm
Once you know your risk, there are concrete steps you can take. Have an emergency kit ready with food, water, and important documents. Create a family communication plan so everyone knows what to do and where to go if you need to evacuate. Securing outdoor items and clearing drains can also help manage water around your property. So, a little bit of planning goes a very long way, you know.
If you're in an area expected to experience significant "high" water, listen to local authorities and be prepared to evacuate when advised. Never try to drive or walk through floodwaters, as even a small amount of moving water can be incredibly dangerous. Remember, safety is the most important thing, and that's something we should all prioritize.
Learn more about hurricane preparedness on our site, and link to this page for essential flood safety tips.
Lessons Learned from Helene's Water Levels
Helene's impact, particularly the extent of its water, offered some tough but valuable lessons for communities and individuals. It really underscored the importance of accurate forecasting and clear communication during a storm. When the water gets "high," as my text puts it, meaning "extending or being far above a base," knowing exactly what to expect helps people make better choices. So, improving how we predict and communicate water levels is a very big deal, actually.
The storm also highlighted the need for resilient infrastructure. Roads and drainage systems that can better handle large volumes of water are essential for minimizing damage and ensuring quick recovery. It's about building stronger communities that can withstand these kinds of events. We saw areas where water management systems worked well, and others where they were overwhelmed, so that's something to think about.
Finally, Helene's water levels showed us that community cooperation and neighborly support are incredibly important during and after a storm. People helping each other through the clean-up and recovery process made a huge difference. So, while the water was high, the spirit of people helping people was, in a way, even higher.
Frequently Asked Questions About Helene's Water
Q: How does storm surge differ from regular flooding?
A: Storm surge is ocean water pushed inland by a hurricane's winds, rising above the normal tide. Regular flooding usually comes from heavy rainfall causing rivers or drainage systems to overflow. So, one is from the sea, the other from rain, basically.
Q: What should I do if my area is forecast for high water levels?
A: If high water is expected, it's really important to follow advice from local emergency services. Secure your home, have an emergency kit ready, and be prepared to evacuate if they tell you to. Safety first, always, you know.
Q: Are flood maps always accurate for predicting water height?
A: Flood maps are very helpful tools, but they show general risk zones based on historical data and models. The actual water height during a specific storm like Helene can vary depending on the storm's exact path, speed, and rainfall. So, they're a guide, but not a precise prediction for every single event, you see.
- Is Emilys Compagno Italian
- What Spider Has The Strongest Fangs
- What Famous Person Is Julia Roberts Related To
Helene by the numbers: How much rain fell in Asheville, Western NC? How

Hurricane Helene by the numbers: Catastrophic destruction covers 400

Lessons Learned from Hurricane Helene - Meridian Magazine Meridian Magazine